Have any questions?
get in touchTel : +86-13641430137
Whatsapp : +86-13641430137
Skype : ourskeeper
E-mail : info@duuhnn.com
Vehicle telematics is an interdisciplinary field that combines telecommunications, informatics, computer science, electrical engineering, and vehicle technology to create a vehicle telematics system that functions to collect vehicle telematics data and derive from it insights and ultimately improve the efficiency and safety of the overall driver experience.
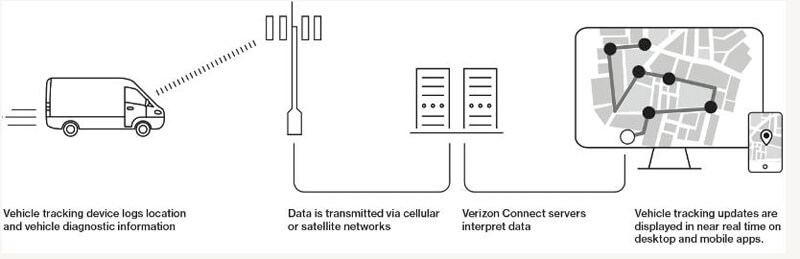
This image depicts the process of vehicle telematics and how data collection is collected and transmitted.
What is in-vehicle telematics?
In-vehicle telematics combines GPS systems, on-board diagnostics, wireless telematics devices, and black box technology to record and transmit vehicle data such as speed, location, maintenance requirements, and repairs, and cross-reference this data with the vehicle's internal behavior. This information can be used for real-time analysis to improve overall driver safety, reduce costs and improve commercial vehicle performance.
What is an in-vehicle telematics system?
Vehicle telematics systems include vehicle telematics devices, which are tracking devices installed in vehicles that facilitate the transmission and storage of telemetry data over a wireless network and the vehicle's own on-board modem and diagnostics (ODBII). Telecommunications companies manage the transfer of information from vehicles and telematics providers to computers or mobile devices, where drivers and fleet telematics managers can access the information.
Vehicle telematics providers typically offer IoT vehicle telematics solutions, a combination of cloud, hardware and software solutions, including GPS tracking, cloud-based platforms that can easily integrate with multiple partners, telematics sensors, fleet Management software, simplified and accessible visual dashboards, reporting capabilities, automated and configurable notifications and alerts, compliance parameters, and real-time AI integration for early warning and instant insights.
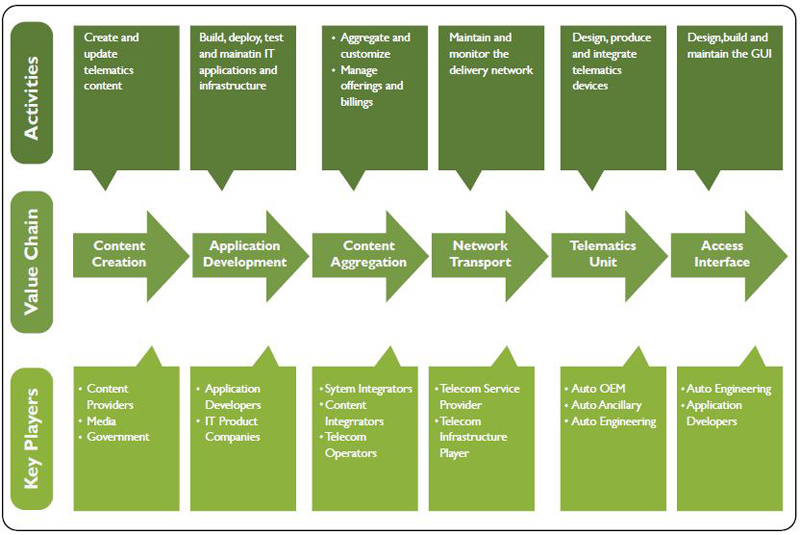
How does an in-vehicle telematics system work?
Telematics devices collect GPS and vehicle-specific data, then transmit the data via General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), 4G and cellular networks or satellite communications to a central server where it is classified, interpreted and optimized for use in in the consumer user interface.
Modern commercial vehicle manufacturers often embed automotive telematics directly into fleet vehicles. Aftermarket GPS devices are also available for installation.
Telematics data typically includes factors such as fuel consumption, idling time, location, speed, hard acceleration or braking, and vehicle malfunctions. The benefits of vehicle telematics analytics include reduced fuel costs, improved driver safety, increased productivity, improved vehicle visibility through precise tracking, data-driven vehicle maintenance planning, maintaining ELD (Electronic Logging Device) compliance, and more precise payroll management.
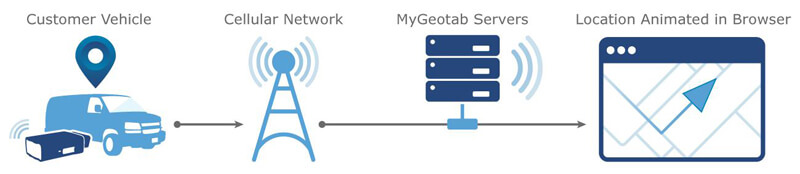
What is vehicle telematics used for?
In-vehicle telematics applications include:
Telematics Vehicle Tracking: In a telematics vehicle tracking system, GPS and on-board GPRS modems communicate with the user and web-based software to transmit vehicle data, which is then converted into information by management reporting tools and mapping software.
Trailer/Container Tracking: GPS devices communicate their location via cell phone or satellite communications.
Fleet Vehicle Telematics Management: Commercial vehicle telematics involves the management of a company's fleet, including vehicle scheduling, financing, maintenance, and on-board diagnostics; driver, fuel, health, and improved safety management; reducing costs, increasing productivity, and maximizing Minimize the risk of vehicle investment and maintain the obligation of compliance with the duty of care.
Telematics Standards: Vehicle telematics providers must adhere to standards developed by the Association of Equipment Management Professionals that enable the delivery of telematics data in a standard xml format.
Wireless Vehicle Safety Communications: Sensors installed in electronic subsystems in vehicles and in fixed locations, such as near call boxes and traffic lights, transmit vital safety information to driver displays over a wider network. This is useful for optimizing routes and fuel usage in company vehicle telematics.
Emergency Alert Systems: Vehicle telematics architectures are open, self-directing structures designed to fuse alert information with nearby vehicles. Telematics emergency alert systems can generate instant autonomous alert notifications in real time using a computer system that updates information at the same rate it receives data, which is especially useful for smart vehicle technology. Silicon micromachined components and radio transceivers work together to facilitate precise, repeatable functions such as emergency warnings

DUUHNN support hardware AI MDVR and ADAS/DMS Camera for video telematics:
